Total Emission
Blackbody
Definition:
- At a given temperature and wavelength, no body can emit more than a blackbody
- Absorbs all incident radiation
- Emits in all directions
Examples:
Example 1 - Sun
| Surface Temperature | |
| Emissive Power | |
| Radius | |
| Radiated Heat | |
| Mass | |
| Specific radiated heat |
Example 2 - Human Body
| Skin temperature | |
| Emissive Power | |
| Surface Area | |
| Radiated Heat | |
| Mass | |
| Specific Radiated Heat |
Spectral Emission
Spectral Emissive Power:
- aka spectral radiant emittance
- Power per unit surface area per wavelength
- Units:
Planck's Distribution:
Wien's Displacement Law:
- Wavelength of peak radiation:
Examples:
Example 1 - Sun
- Surface temperature:
- Peak radiation at:
(visible range)
Example 2 - Human Body
- Skin temperature:
- Peak radiation at:
(infrared)
Example 3 - Earth
- Average air temp:
- Range:
(Infrareds)
Example 4 - Flame
- Burnt temperature:
- Peak radiation at:
(infrared)
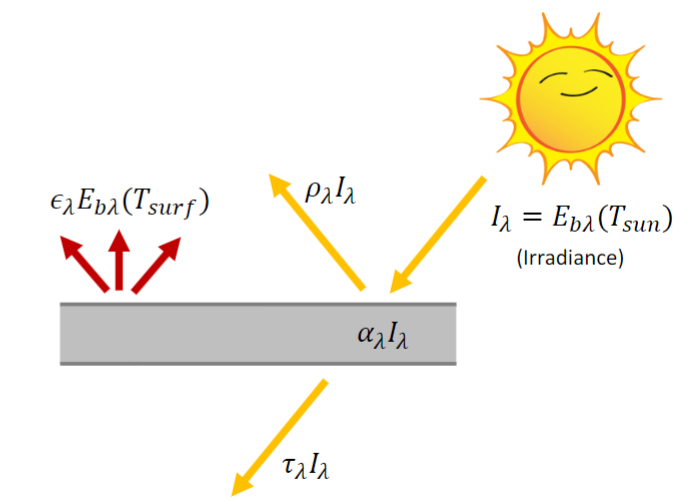
Non-Blackbody
Definitions:
- Absorptivity (
) - Fraction of incident radiant energy absorbed by a surface - Reflectivity (
) - Fraction of incident radiant energy reflected by a surface - Transmittivity (
) - Fraction of incident radiant energy passing through surface - Emissivity (
) - Fraction of blackbody radiation emitted by the surface
Key properties:
- Reflected and transmitted at same wavelength
- Emitted at different wavelength
Special case: Blackbody
Kirchhoff's Law:
Examples:
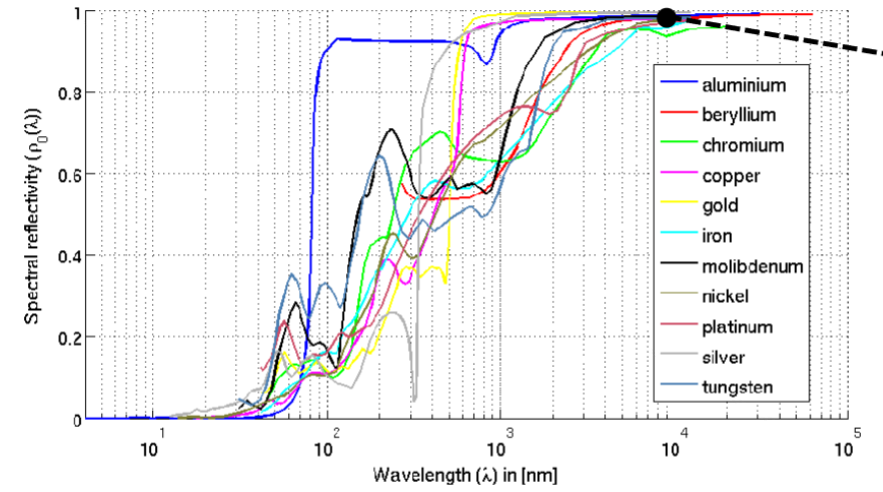
Example 1: Metals
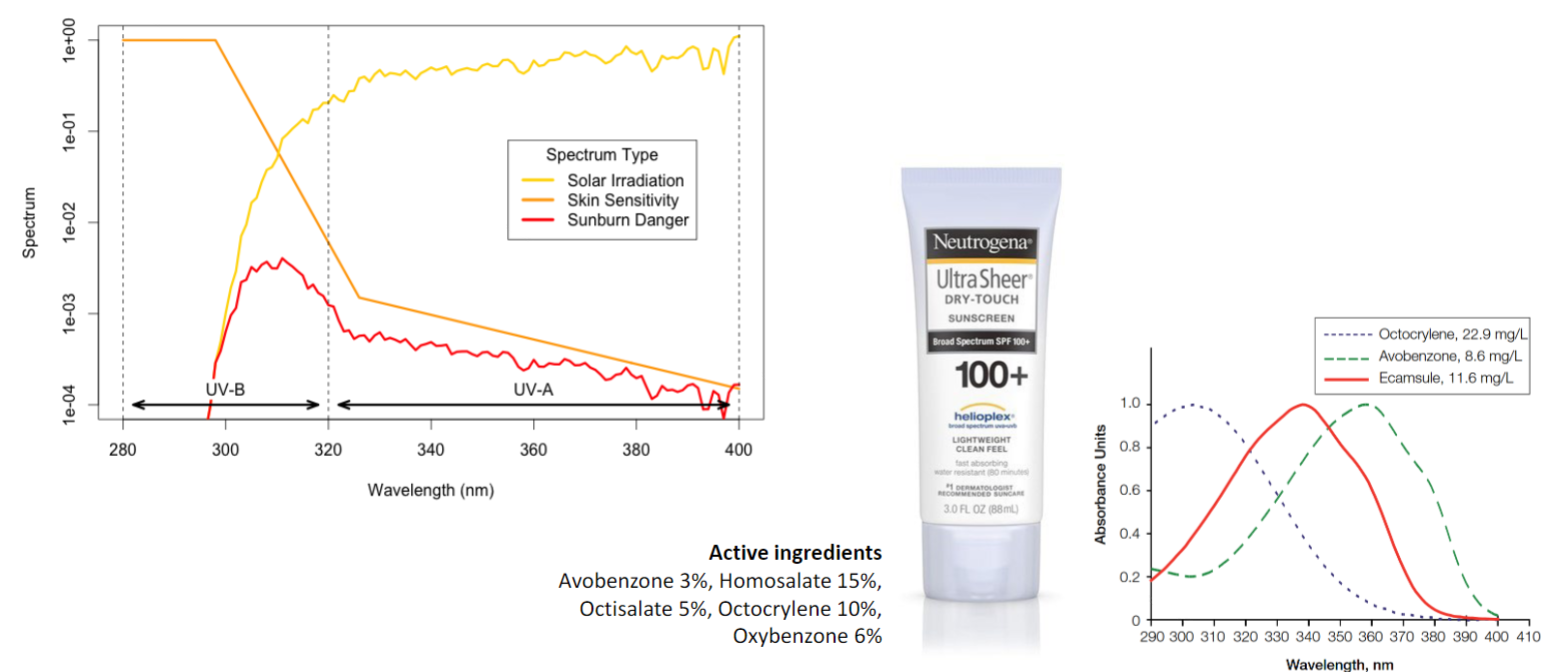
Example 2: Sunscreen
Example 3: Human Skin
Values:
- Skin temperature:
- Peak radiation:
(infrared)
Special case: Gray body
- Not color gray
- Constant Emissivity: