Otto Cycle
Facts:
Key operating facts:
- Power control
- More air
More Power
- More air
- Fuel Injection
- Intake Stroke
Combustion:
- Constant air/fuel ratio
- Close to stoichiometric
- Premixed mode
- Start of combustion controlled by spark ignition
- Front propagation
Pros/Cons:
- Subject to knocking
need high octane # fuel
Ideal Otto Cycle:
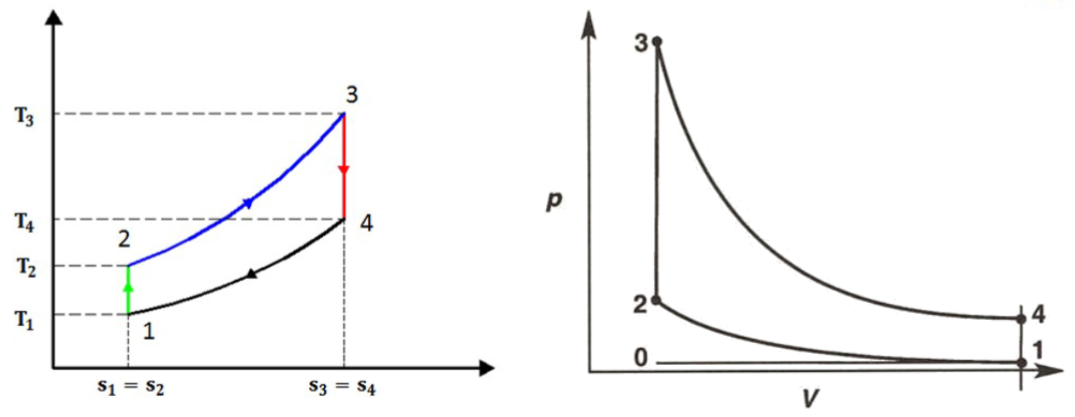
Process:
Intake Stroke:
: constant pressure
Compression Stroke:
: isentropic : combustion, constant volume
Power Stroke:
: isentropic
Exhaust Stroke:
: constant volume : contant pressure
System:
- Unit mass inside combustion chamber
- Intensive/specific quantities
- Compression ratio
First Law of Thermodynamics:
: : : :
Second Law of Thermodynamics:
: :
Specific heat added:
- Heat released by combustion
Specific work produced:
- Power Stroke - Compression Stroke
Thermal Efficiency:
- Not a function of any temperature
- Independent of any heat added
Sources of Irreversibility:
- Combustion:
- Uncontrolled expansion: