Mixtures
Need more than 2 Intensive variables.
Mixing Rules
Specific Volume:
Internal Energy:
Enthalpy:
Entropy:
Fractions
Mixture of
Independent of EOS
- Mass of component
: - Amount of component
:
Totals:
- Total mass:
- Total amount:
Fractions:
- Mass fraction:
- Mole fraction:
Molecular Weights:
Molecular Weight:
- Component
: - Mixture:
Relations:
- Molecular weight:
- Mass fractions:
- Mole fractions:
Energies:
Extensive variables:
Simply add them up.
Intensive variables:
Use mixing rules:
Heat Capacities:
- Updated definition:
- Mixing rules:
Molar quantities:
- Same math
where , are per mole.
Dalton Model:
Gas + Vapor Mixture:
Defintions:
- Gas: substance that does not do any phase changes (exit in single phase)
- Ex: air
- Vapor: gaseous form of a substance that also exists in liquid form
- Ex: water
(Common) Assumptions:
- Gaseous phase = mixture of ideal gases
- No dissolved gases in solid/liquid phase
- Equilibrium between condensed/vapor phase independent of other gases
Saturated mixture:
- If vapor partial pressure is saturation pressure
- Cannot have more vapor!
Dew Point:
- Temperature when air is saturated with water vapor
Relative humidity (RH):
- Ratio of mole fraction of vapor over mole fraction when it is saturated
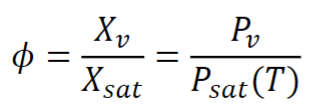
Humidity ratio:
Also known as specific humidity or absolute humidity, it is the mass of water per kilogram of dry air.
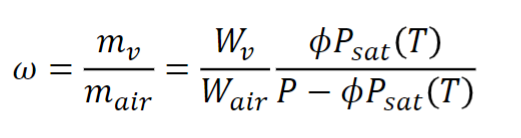
Example: Dehumidifier
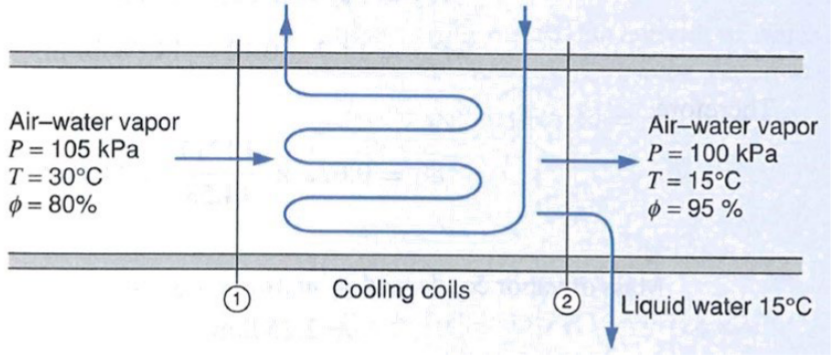
Assumptions:
- Steady State
- Ideal Gases: air, water vapor
Incoming Mixture:
- Partial Pressure:
- Humidity ratio:
Outgoing Mixture:
- Partial Pressure:
- Humidity ratio: