Internal Combustion Engine
History:
Components:
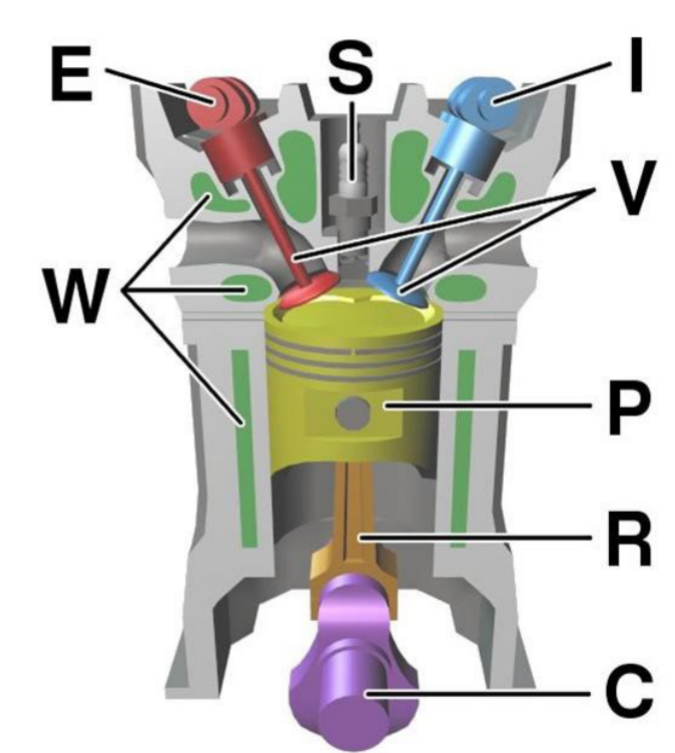
- E: Exhaust camshaft
- I: Intake camshaft
- S: Spark plug
- V: Valves
- P: Piston
- R: Connecting Rod
- C: Crankshaft
- W: Water jacket for coolant flow
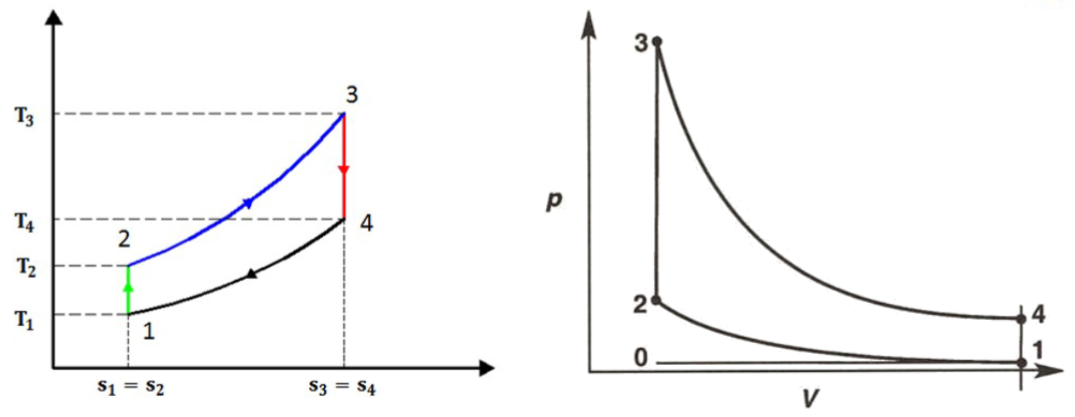
Cycles:
General Process:
Intake:
- Fresh air comes in
- Constant Pressure
Compression:
- Compression of fresh gases
- Isentropic (adiabatic reversible)
Power:
- Combustion at Constant Volume or Constant Pressure
- Followed by Isentropic expansion
Exhaust:
- Expel burnt products
- Constant Pressure
Otto Cycle:
Diesel Cycle:
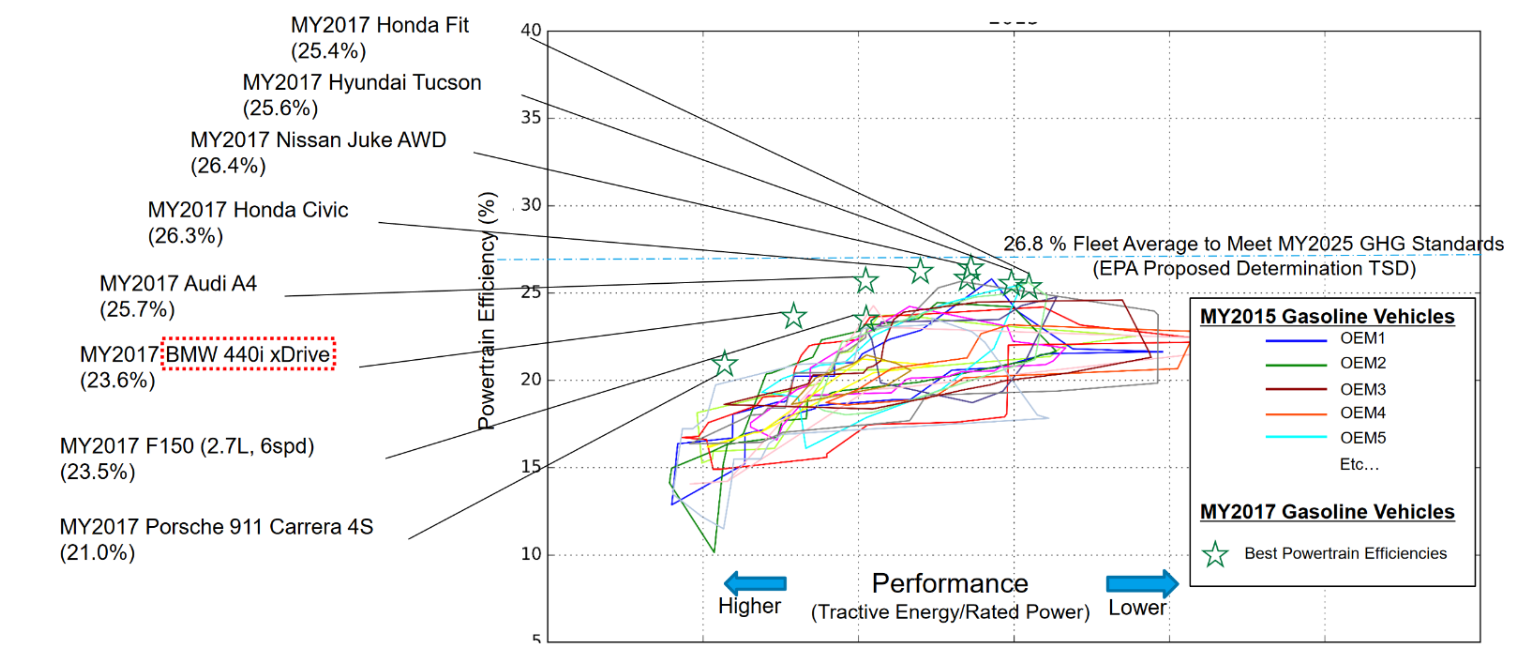
IC Engine Efficiencies:
Theoretical Efficiency: (
- Otto Efficiency
- Assumptions: same gas/properties
Real gas efficiency: (
- "Otto" Efficiency
- Consider changes in gas properties
Indicated efficiency: (
- Measured efficiency for the real Otto Cycle
- Heat losses, finite rate chemistry, pumping losses...
Powertrain efficiency: (
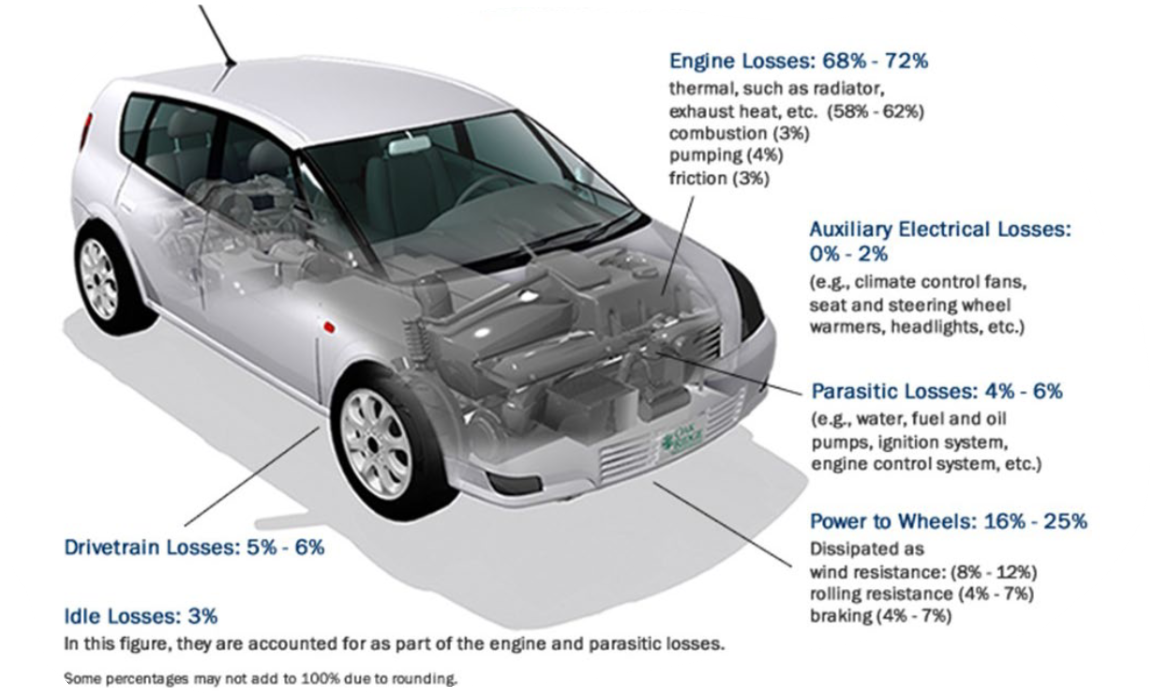
- Ultimate/Final
- Measured on the drivetrain
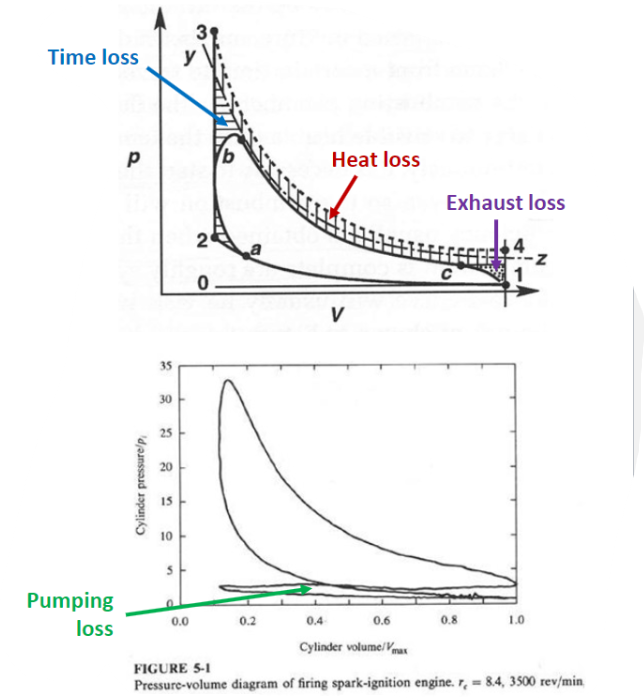
Time loss:
- Finite rate chemistry/flame propagation
- Start:
- BTC (Point a) - Stop:
- ATC (Point b) - 30% of the difference between
and
Heat loss:
- Compression: small heat loss (low T)
- Expansion: large heat loss (high T)
- 60% of the difference between
and
Exhaust blowdown loss:
- Valve opens:
- BBC (Point c) - 10% of the difference between
and
Pumping Loss:
- Getting air in/out
pressure difference - Full load:
MPa small loss - Idle:
MPa large loss