Conduction Heat Transfer
Conduction = Heat Transfer
- Through matter (solids, liquids, gases)
- Without bulk motion
Recall: Definition of Heat
Energy transferred across boundaries of system due to temperature difference.
Important People:
Conductivity
Defintions:
- Conductivity:
( ) - Thermal Diffusivity:
( )
Fundamental Property of Fluid:
- Independent of motion
- Depends on composition
- Depends on
and
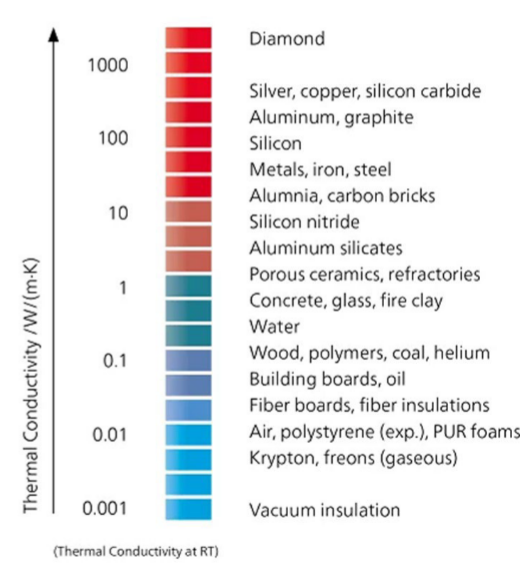
Conductivity Table:
| Material | Conductivity ( |
|---|---|
| Air | 0.0235 |
| Water | 0.6 |
| Silver, Pure | 418.0 |
| Copper 11000 | 388.0 |
| Aluminum 6061 T6 | 167.0 |
| Zinc, Pure | 112.2 |
| Iron, Cast | 55.0 |
| Solder, 60% Tin | 50.0 |
| Titanium | 15.6 |
| Thermal Grease, T660 | 0.90 |
| Fiberglass | 0.040 |
| Air, stp | 0.025 |
 |
Examples:
Example 1:
How much heat transfer between two surfaces at two different Temperature?
Configuration:
- Two very large flat plates
- Temperature difference between plates
- Steady State
Key Observation:
- Heat lost by hot plate = heat gain by cold plate
Same heat transfer Constant heat flux
Key Conclusions:
- Linear temperature:
- Heat flux:
- Newton's Coefficient:
Example 2:
How much heat transfer between two surfaces at two different temperatures?
Configuration:
- Two spherical surfaces
- Temperature difference between surfaces
- Steady State
Key Observation:
- Heat lost by hot oven = heat gain by cold turkey
Same heat transfer Heat Flux
Key Conclusions:
- Temperature:
- Heat flux:
Example 3:
Assumptions:
- No convection heat transfer
- All doors and windows closed
- No outside wind
- No Radiation Heat Transfer
- All outside walls shaded
Setup:
- System =
- Uniform temperature inside the house
- Uniform temperature outside the house
- Quasi Steady State (within walls)
- Constant Pressure
First Law of Thermodynamics:
- Mass of "stuff" inside (air, furniture, ...):
- Ceiling area:
- Attic temperature:
- Area of outside walls:
- Outside temperature:
Heat Transfers:
32% (attic) + 68% (walls + windows)